What is RDX Basic Chemistry of RDX
RDX (Research Department Explosive), commonly known as hexogen, is one of the most important high-energy nitroamine compounds. With the molecular formula C₃H₆N₆O₆, it contains a densely packed oxygen–nitrogen network made up of a six-membered ring bonded to three nitro (–NO₂) and three nitramide (–N–NO₂) groups; this network generates extraordinarily high pressures and temperatures upon detonation. Found as a crystalline white powder, RDX begins to melt at 204 °C yet is more sensitive to impact and friction than TNT. However, its high chemical stability means that when mixed with suitable binders (e.g., the plasticizers in C4), it becomes both safe and high-performing.
Summary Items
- Molecular Formula: C₃H₆N₆O₆
- Chemical Class: High nitroamine (nitramide) explosive
- Crystal Density: ~1.82 g/cm³
- Melting Point: ~204 °C (pre-decomposition)
- Physical Appearance: White, needle-like crystals
Discovery and History of RDX
First reported in 1899 by British chemist G. C. Hale, large-scale production of RDX accelerated on the eve of World War II. During the war, the U.S. and U.K. produced tons of RDX via the Woolwich–Bachmann process, powering torpedoes, depth charges, and armor-piercing warheads in mixtures such as Torpex and Cyclotol. After NATO standardization in the 1950s, RDX became the main component of plastic explosives like C4; today, research continues on nano-scale RDX crystals for optimizing unmanned system munitions.
Key Milestones
- 1899: First laboratory synthesis (England)
- 1940–1945: Bachmann process enables mass production
- 1956: Adopted as principal component in C4 formulations
- 1990s: Full-scale tests confirm RE factor of 1.60
- Present: Integration of nano-RDX in tri-phase composite warheads
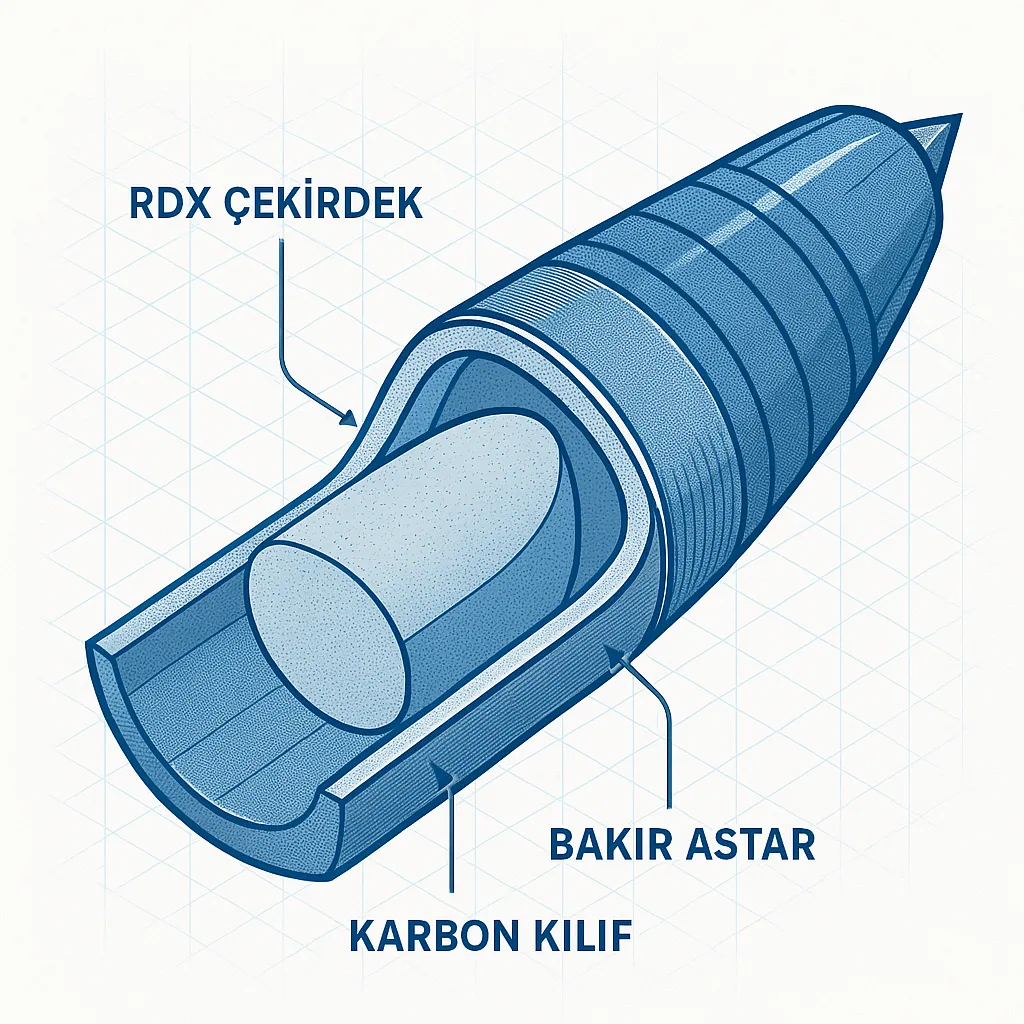

Physicochemical Properties of RDX
Detonation Velocity and Energy Density
RDX outperforms TNT with a detonation velocity of approximately 8 750 m/s and a chemical energy of 6.8 MJ/kg (versus TNT’s 6 900 m/s and 4.6 MJ/kg). Its reference explosive factor (RE) is ~1.60, meaning equal mass of RDX delivers 1.6 times the destructive effect of TNT. This enables the same—or greater—shock wave from smaller munition bodies, saving weight in modern missile warheads.
Sensitivity and Stability
While RDX is more sensitive than TNT to heat and friction, it resists chemical aging. Its low volatility eliminates vapor-loss concerns during long-term storage; however, impact tests can trigger detonation at energy levels of 7–8 J, so professional handling protocols are essential. When bound into plastic formulations (like C4), its impact sensitivity is dramatically reduced.
RDX Role in the Defence İndustry
RDX’s high energy output makes it the core ingredient of the most advanced munitions. ArrowDefence R&D teams conduct performance tests on RDX-based composites ranging from missile warheads to unmanned ground vehicle charges.
Missile and Rocket Warheads
In armor-piercing or fragmentation warheads requiring high shock waves, RDX forms supersonic shaped jets in alloy steel liners, increasing homogeneous armor equivalent (RHAe) penetration capability.
Precision Munitions and Shaped Charges
In explosively formed penetrators (EFP) and linear cutting charges, RDX is combined with moldable binders to achieve millimeter-precision cuts and minimal collateral damage. This makes it ideal for critical infrastructure or base demolition missions requiring controlled destruction.

Civilian and Industrial Uses
RDX’s high detonation velocity also offers advantages in the civilian sector. Deep-sea seismic surveys use RDX-based charges to generate powerful pressure waves in limited volumes; micro-RDX boosters are used to sever separation bolts in satellite deployment systems. In mining, RDX acts as a booster for ammonium nitrate–based ANFO mixtures.
Usage Summaries
- Deep-sea seismic mapping
- Satellite separation bolt charges
- ANFO booster capsules in mining
- Research shock-tube detonations
Production Process and Safety
Industrial production of RDX follows the Bachmann or E-process, based on hexamine nitration. The process involves controlled temperature management in a mixture of nitric acid, ammonium nitrate, and acetic anhydride. Under ISO 9001:2015 and AQAP 2110 quality protocols, acidic waste is recovered and neutralized per environmental regulations.
- Hexamine Dissolution
- Controlled Nitration & Crystallization
- Centrifugal Washing
- Drying & Screening
- Stabilization Testing
Storage and Transportation Standards
Classified as UN 0072, hazard group 1.1D, RDX must be stored at 10–30 °C and ≤ 55 % relative humidity. Copper grounding bars to prevent static and FM-200 gas fire-suppression systems are recommended. ArrowDefence’s logistics chain adheres fully to NATO-AC/258 shipping procedures.
Environmental Impact of RDX
Due to its high nitro content, RDX residues pose ecotoxic risks if they leach into soil and groundwater. Studies show certain bacterial strains can degrade RDX into nitrate and formaldehyde, offering potential bioremediation solutions to reduce cleanup costs. Meanwhile, neutralization of production waste and closed-loop water recovery remain indispensable components of environmental compliance.
Conclusion and ArrowDefence Solutions
What is RDX? The most comprehensive answer: a high-energy, versatile explosive that drives modern defense technology. Its chemical structure makes it ~60 % more powerful than TNT; when combined with plastic binders, operational safety increases.
At ArrowDefence, we provide end-to-end R&D, testing, and consultancy covering RDX’s full lifecycle—from production to field integration. Whether your project involves precision munitions or deep-sea blasting, our expert team will optimize the ideal formulation and safety protocols for you.



